Frequent causes
Causes
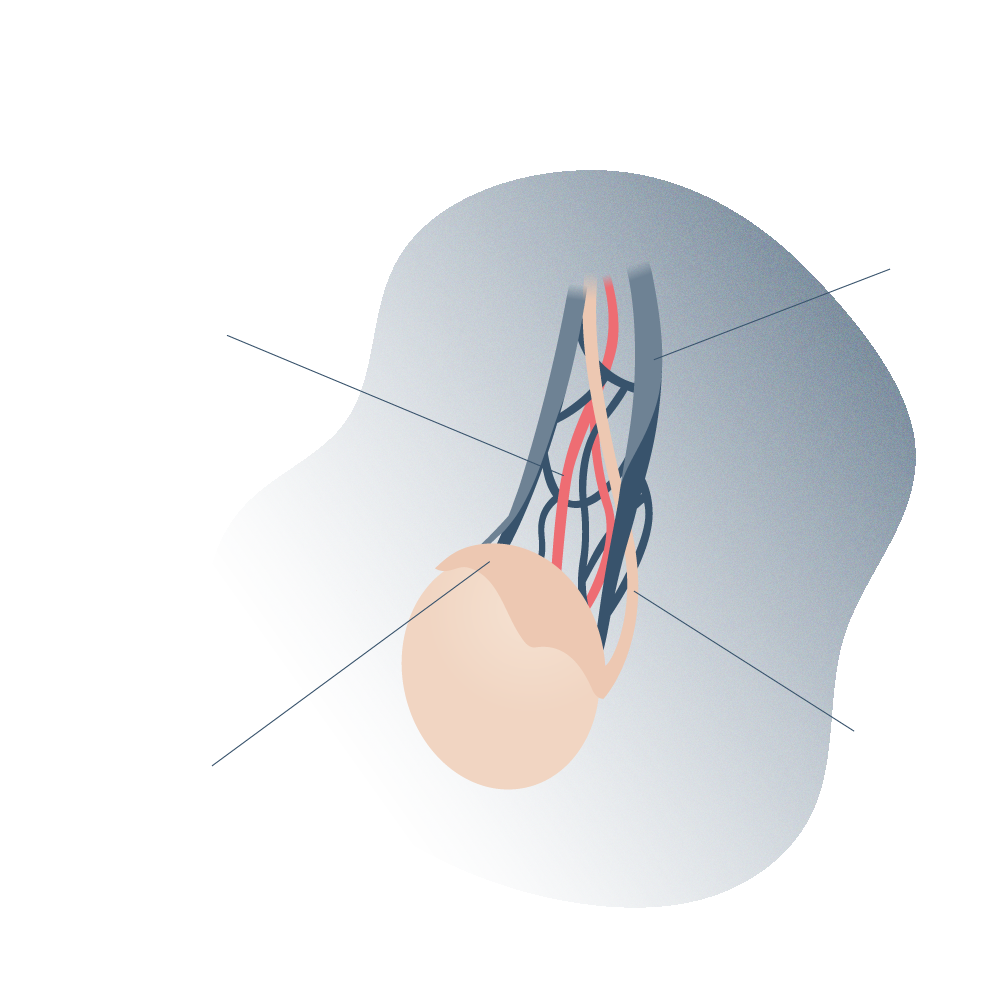
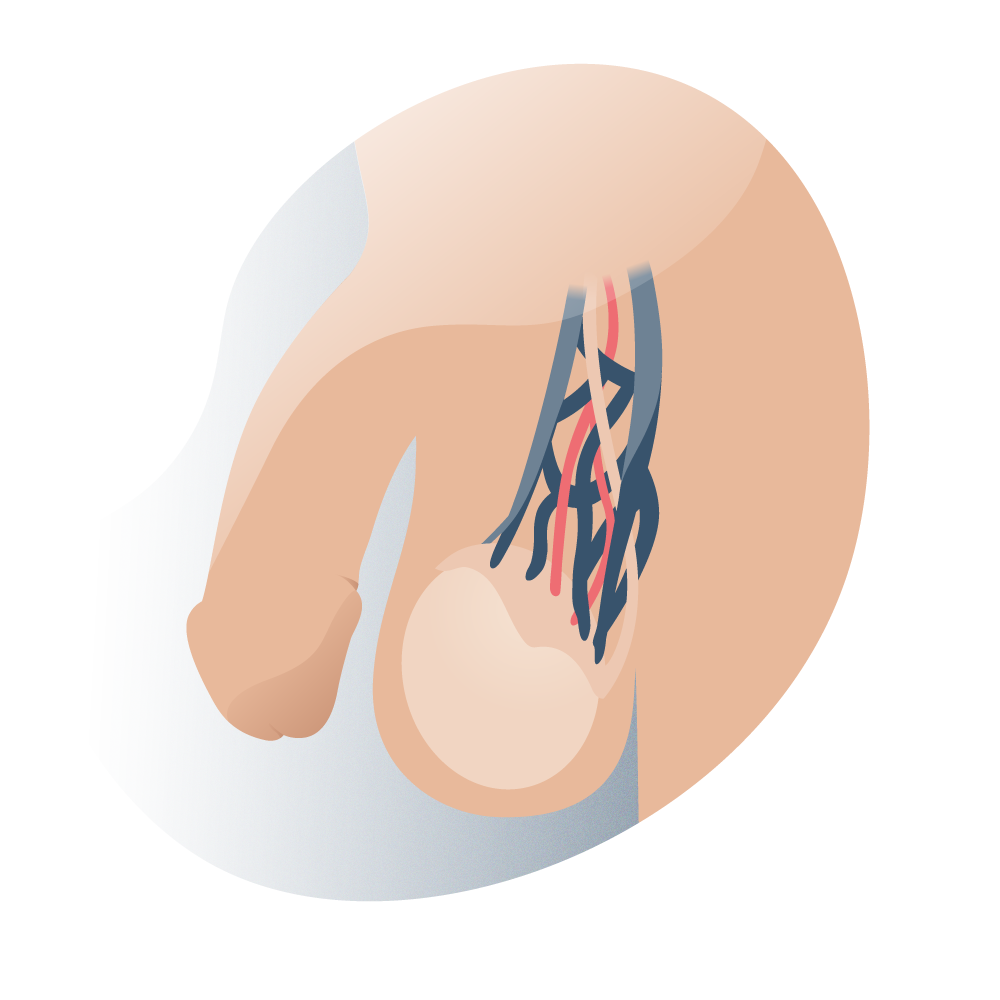
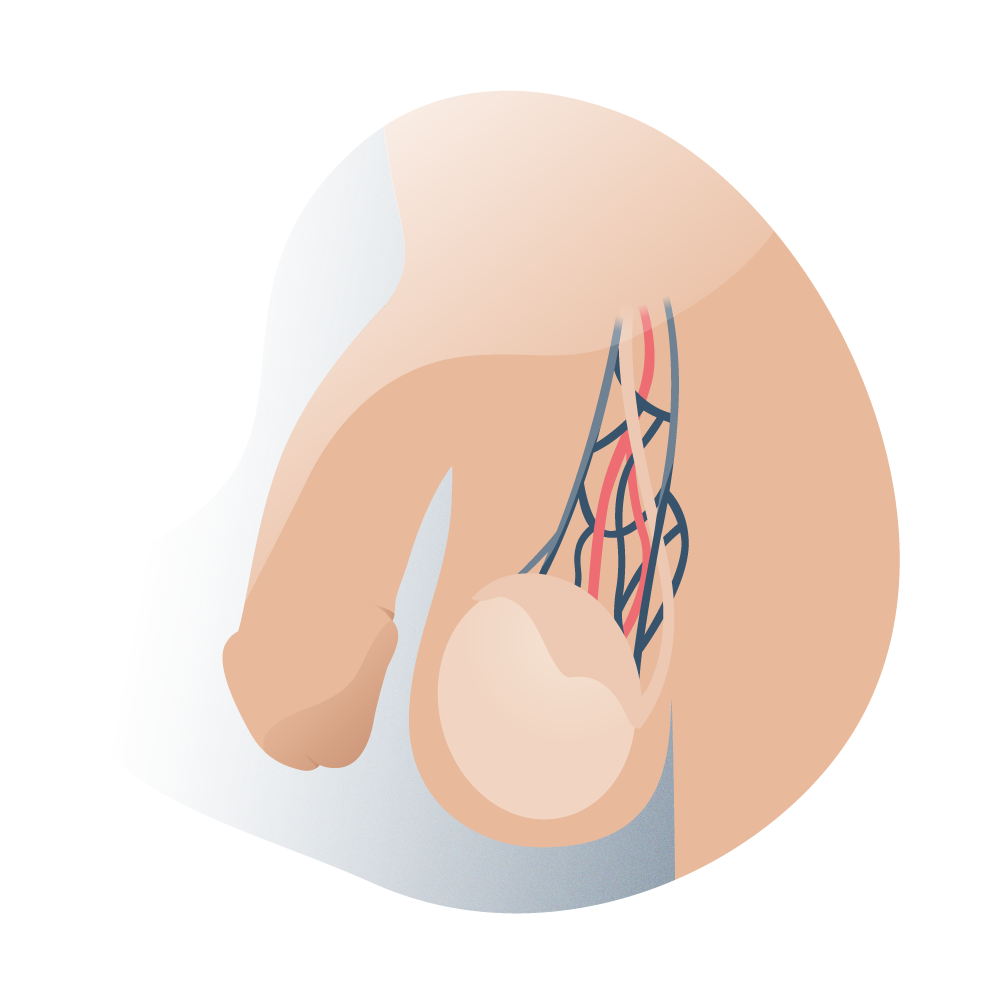
It is considered a multifactorial pathology, whose aetiology is not totally defined, however, the frequency of varicocele is much higher on the left side, in 90% of the total cases, for this reason, it has been correlated with alterations in the venous drainage of the left testicle, finding venous reflux and increased pressure in the drainage of the left spermatic vein to the renal vein on the left side.
Among the possible causes that would explain this dysfunction in patients with varicocele are:
- Absence of venous valves in the left testicular vein, which would give rise to venous reflux and varicose vein formation.
- Increased hydrostatic pressure and length of the left testicular vein as it empties into the left renal vein.
- Compression of the left testicular vein by the superior mesenteric artery and the abdominal aorta.
Varicocele e infertilidad
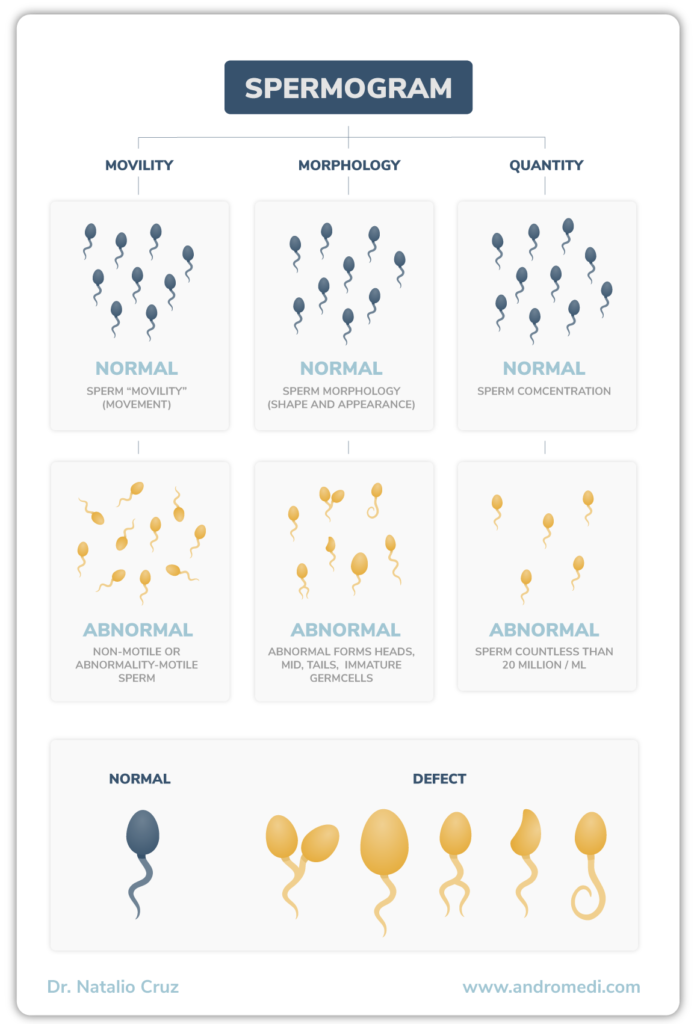
Since 1880 a relationship between the presence of varicocele and infertility was discovered, this could be explained by the modifications at the level of tissue and testicular function that occur in this disease.
For normal sperm development, a temperature of approximately 33°C is required. At this temperature, the DNA suffers less oxidative damage, and therefore there is less chance of genetic mutation; this explains the scrotal location of the testicles. In addition to the strategic anatomical location, the pampiniform plexus helps to cool the blood coming from the testicular artery, thus contributing to the optimal temperature required by the testicles. For this reason, any alteration in the veins and consequently varicocele contributes to the increase of the scrotal temperature and deficiencies in the quality of the sperm.
Andromedi pertenece a las organizciones médicas más destacadas en el sector de la Uro-Andrología