FRequent causes
what causes it?
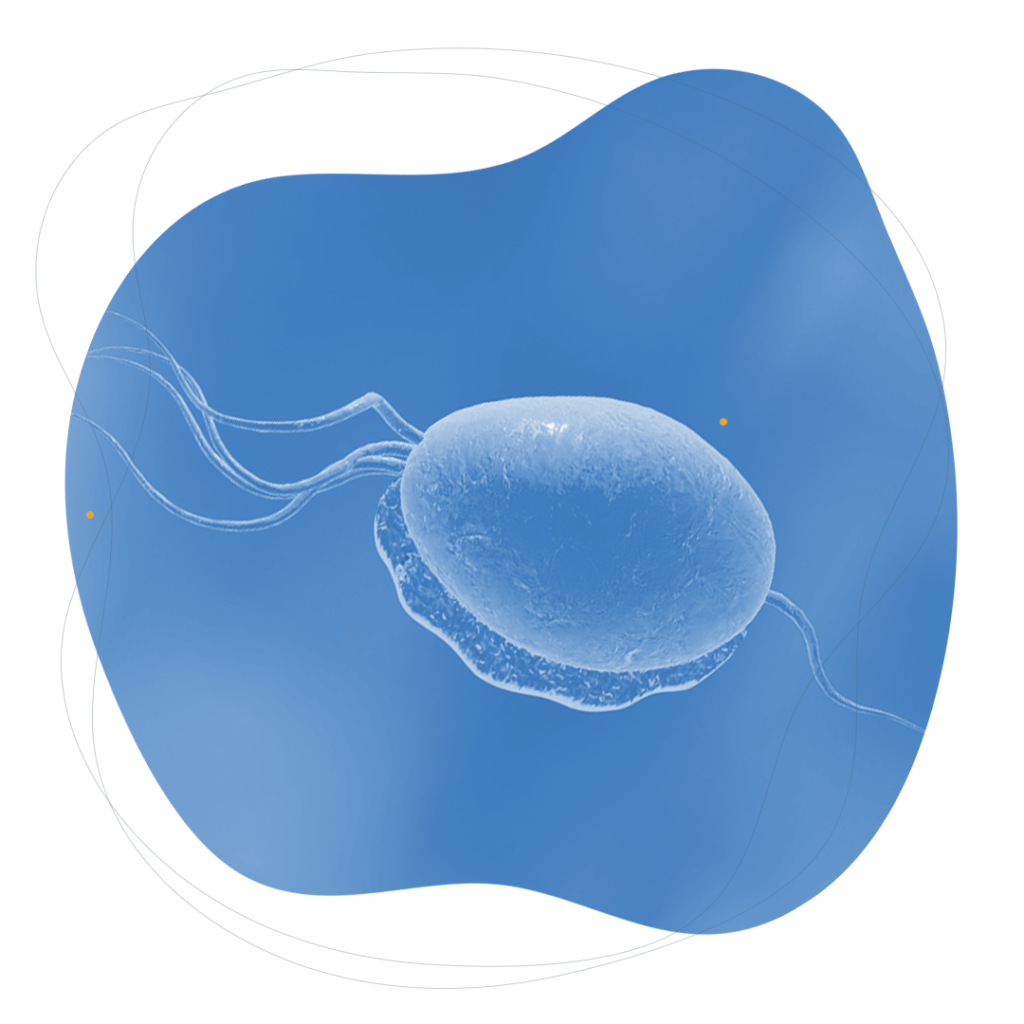
Trichomoniasis is caused by a tiny intracellular parasite called trichomonas vaginalis, which is sexually transmitted, by contact with mucous membranes.
The time from infection and the development of signs and symptoms of the disease is about three weeks. This increases the risk of infecting other people during this period.
The male genitourinary tract is the only natural reservoir of this parasite, so there is no likelihood of contracting this disease from the environment.
Trichomoniasis is caused by a tiny intracellular parasite called trichomonas vaginalis, which is sexually transmitted, by contact with mucous membranes.
The time from infection and the development of signs and symptoms of the disease is about three weeks. This increases the risk of infecting other people during this period.
The male genitourinary tract is the only natural reservoir of this parasite, so there is no likelihood of contracting this disease from the environment.
This sexually transmitted infection (STI) is transmitted through direct contact of the genital mucous membranes during vaginal, anal or oral sex, even when symptoms have not started to occur in the patient.
The body area most predisposed to acquiring the parasite is the lower part of the female genitals (vagina, vulva, and urethra) in women and the urethra in men. Because the parasite needs a human cell to feed and survive, there is no risk of getting the disease in swimming pools, public restrooms, or by sharing towels or used clothing.
Transmission can occur from the penis to the vagina or vice versa.
Andromedi pertenece a las organizciones médicas más destacadas en el sector de la Uro-Andrología