Medical evaluation
Classification
Congenital: within the congenital hydroceles we have:
It is produced by an incomplete closure of the tunica vaginalis during growth, maintaining communication with the peritoneal cavity. This causes the liquid to flow from the abdomen into the scrotum and vice versa.
On examination, it can be seen how this accumulation of fluid can increase in size during crying, Valsalva manoeuvre or straining and fluctuates during the day and night.
It usually appears in children older than one year, after some action that has increased their intra-abdominal pressure. It does not heal spontaneously, for this reason, the solution is surgical since its persistence could alter the testicle by compression or become an inguinal-scrotal hernia.
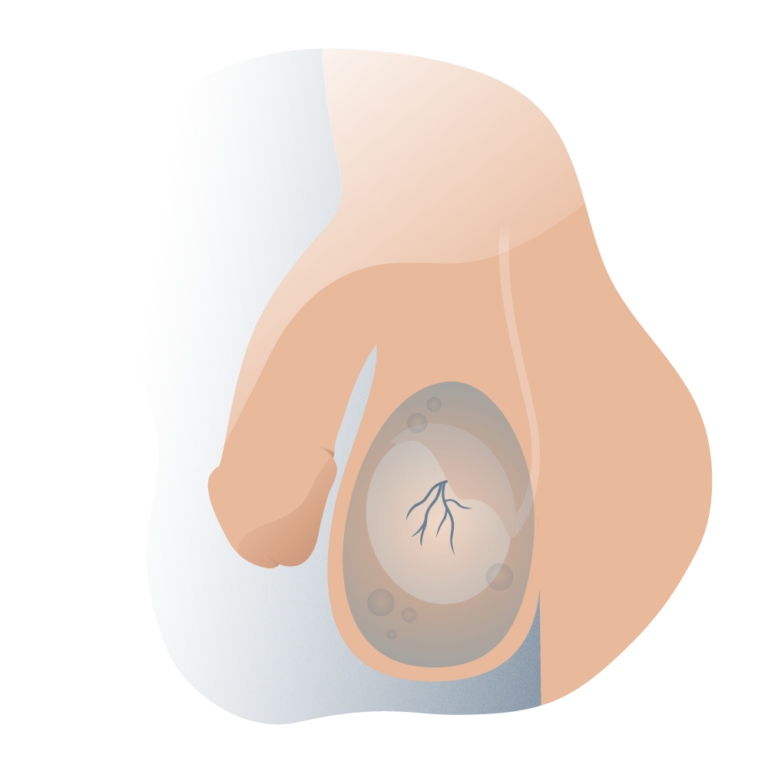
This is the most frequent hydrocele, it is produced when the tunica vaginalis closes with a large amount of liquid from the peritoneal cavity and this is not absorbed, it is typical of newborns, in most children it heals spontaneously before the first year of life since the liquid trapped between the two layers of the testicular tunica vaginalis is reabsorbed and there is no communication with the peritoneal cavity.
This is an idiopathic hydrocele that has no known cause. It is attributed to an imbalance between the capacity of the visceral and parietal layers of the tunica vaginalis to secrete and reabsorb; it usually occurs in older adults.
it occurs as a consequence of a traumatic or infectious event at the testicular level, such as inguinal hernia, inguinal surgery, Filariasis, epididymitis, orchitis and other traumatic causes.
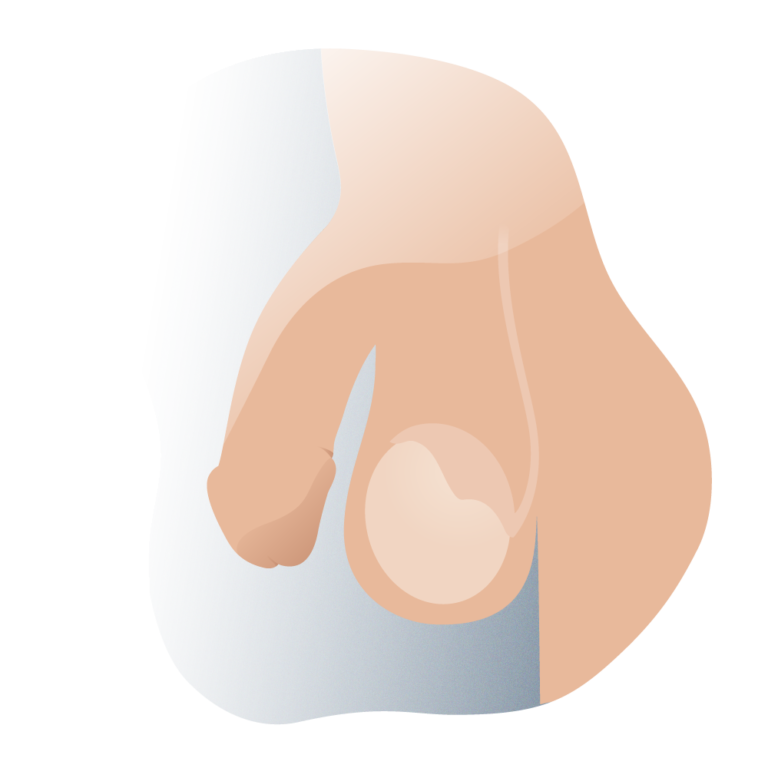
It is formed by a very thin persistence of the peritoneal vaginal duct, which causes a collection of liquid in the inguinal duct, which does not affect the testicle. Clinically, it is observed as a mobile, round, irreducible and painless mass in the upper part of the scrotum or in the inguinal canal, and generally appears during the first months of life.
this is a type of hydrocele with a very low incidence, which consists of a collection of fluid at scrotal level but which is continued through the inguinal canal and the abdominal cavity.
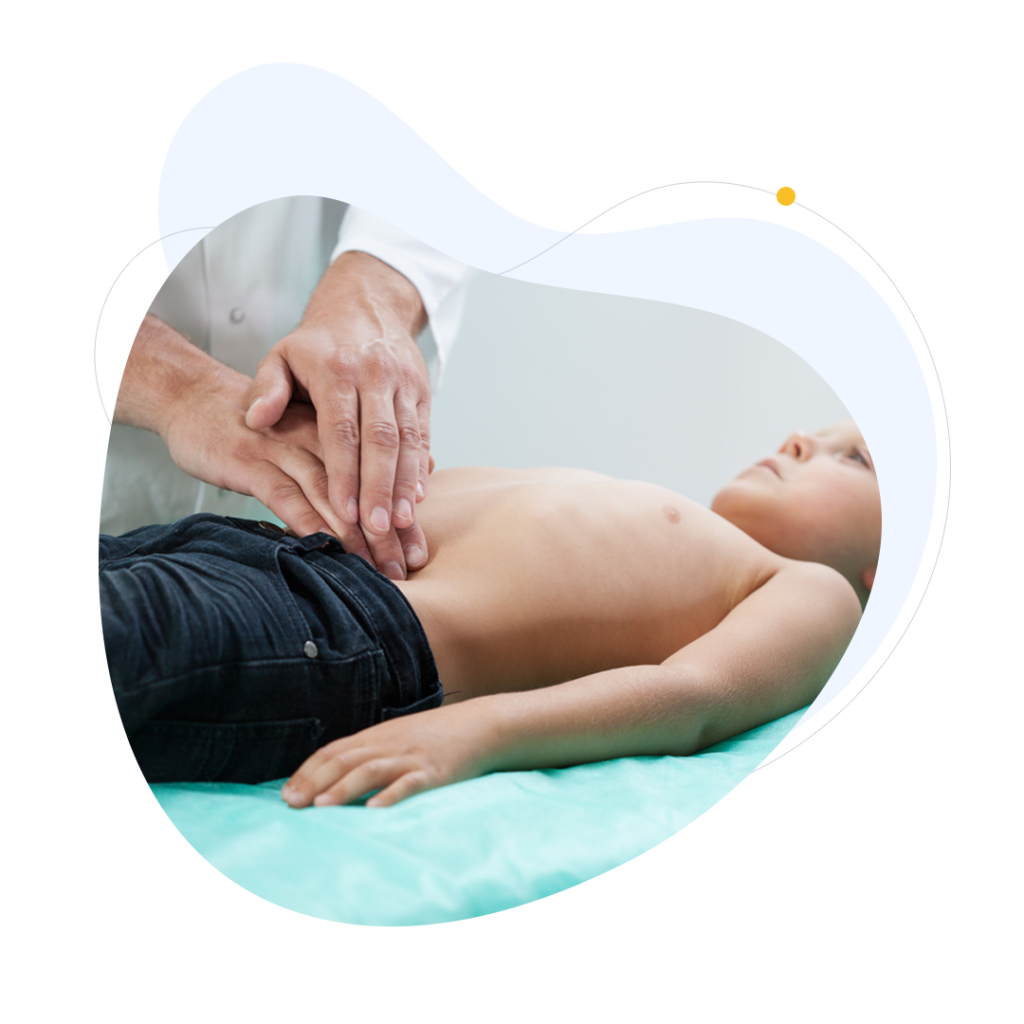
It is usually present from birth and progresses over time. Upon physical examination, it can be seen that compression of the abdominal mass produces enlargement of the scrotal mass and vice versa.
Its solution is surgical, due to the compressive nature of the hydrocele to the testicular mass.
Andromedi pertenece a las organizciones médicas más destacadas en el sector de la Uro-Andrología