The after-effects of a prostatectomy are often severe.
When a patient receives the news at the specialist’s office that he must undergo TUR (trans-urethral resection), he is often unaware that it is a medical condition that will affect him in the medium and long term in his daily life.
We are talking about the so-called prostatectomy or in other words, the cutting and removal of tissue belonging to the prostate gland. We are no longer surprised, as we are used to it, but it is hard to believe the amount of patients who come to our office in Seville with problems of incontinence or impotence derived from this intervention who had not been informed of the possible (probable) sequelae.
As we will see in this article, many of these side effects may have a subsequent treatment, but even so, we believe that these should always be known by the patient in the first instance, so that they can always assess and are aware of the step they are going to take.
What is the prostate and what diseases affect it?
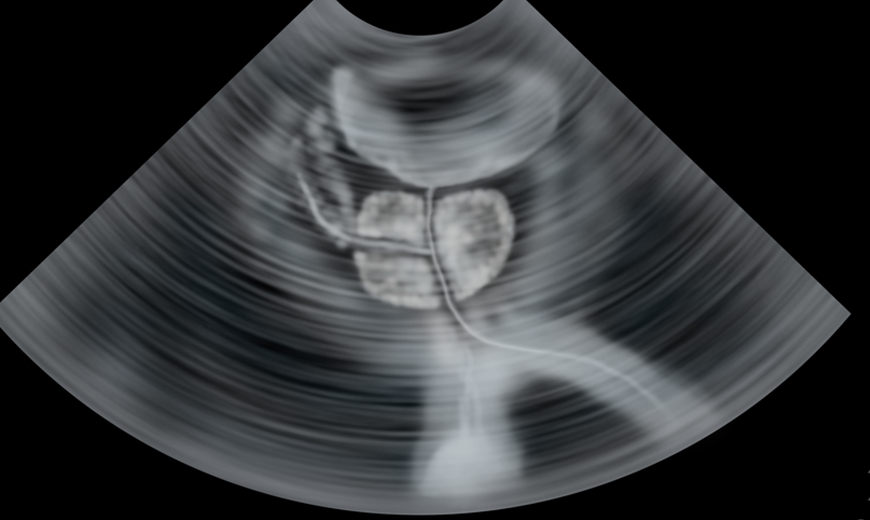
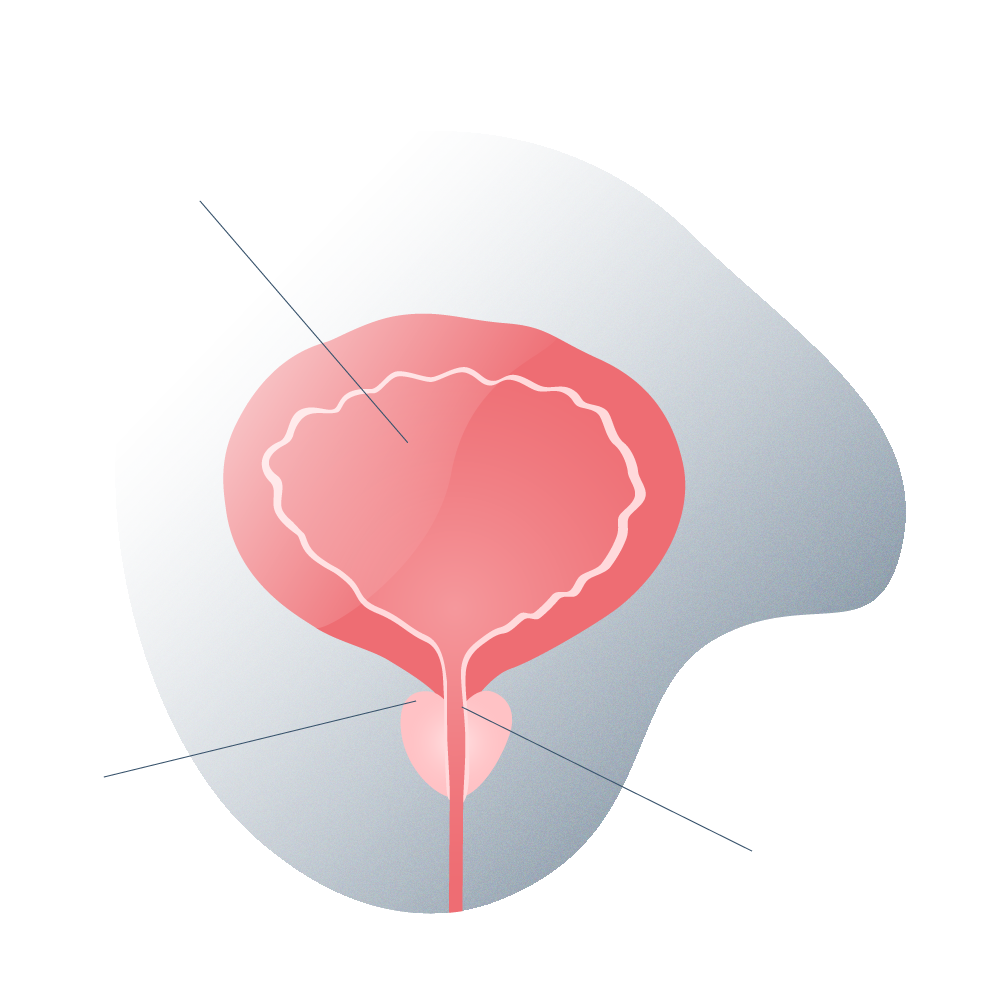
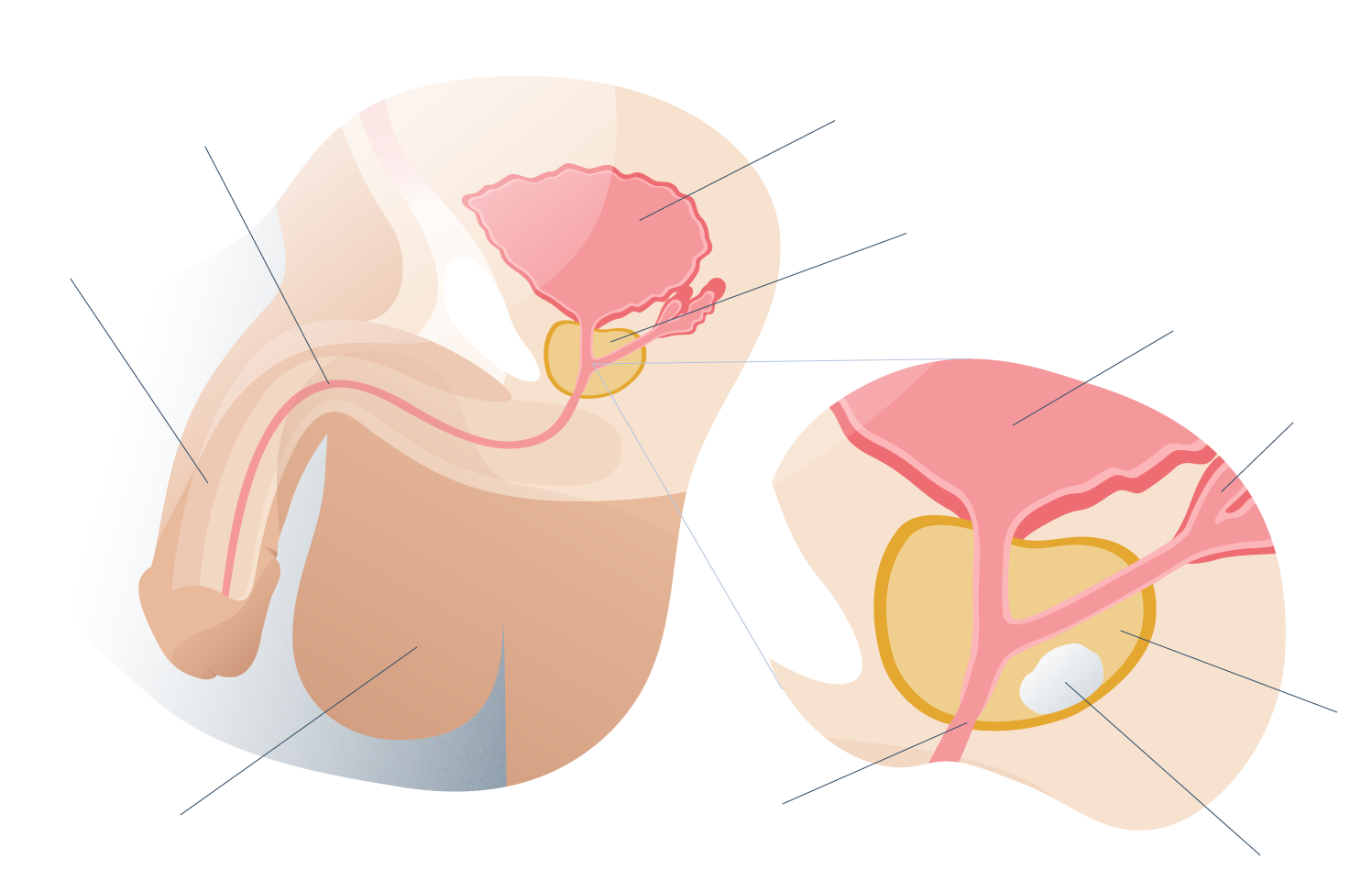
The prostate is a glandular organ located in front of the rectum, below and at the exit of the urinary bladder, whose function is to generate part of the fluid that man secretes in ejaculation, and which serves as a means of transporting sperm.
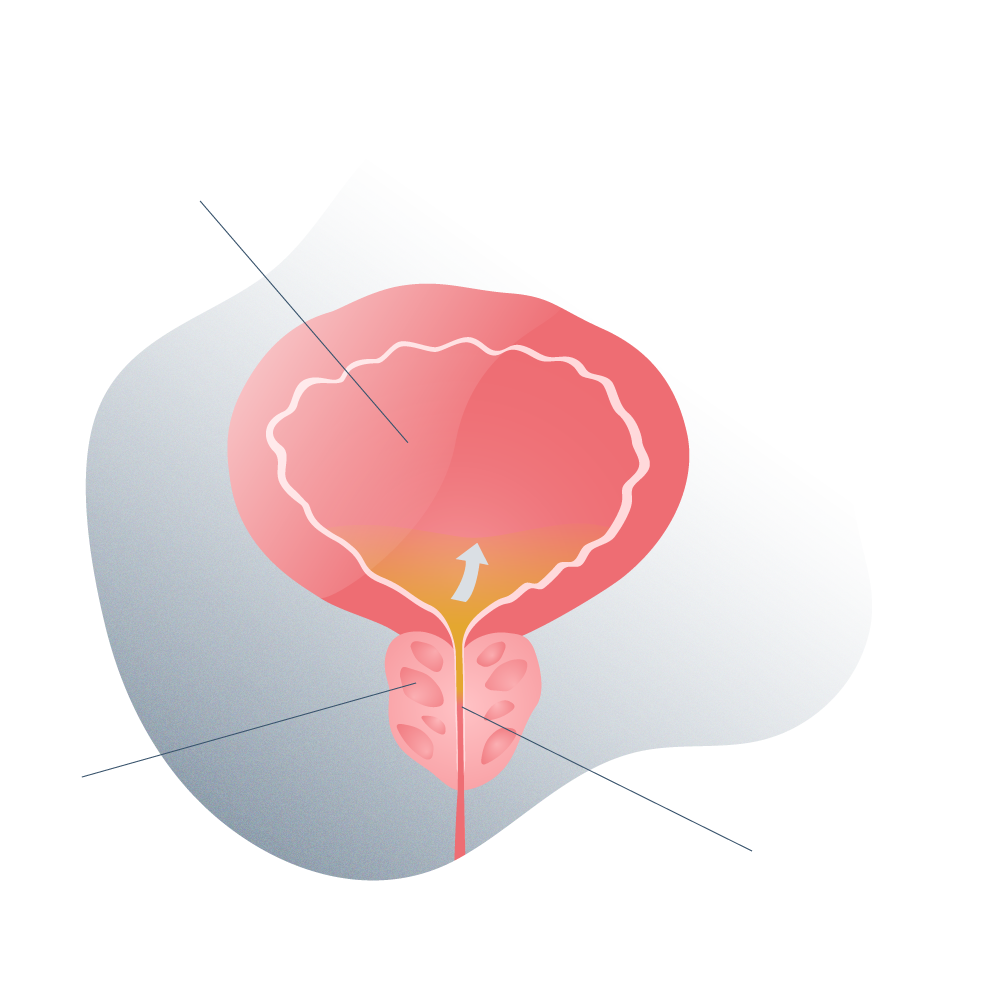
The abnormal or disordered increase in size suffered by an organ or an organic tissue due to the increase in the number of normal cells that form it, is what we call hyperplasia, which in practice is known commonly as hypertrophy. It should be noted that prostatic hyperplasia, although it may sound like it because of the “abnormal increase in cells” is not a cancer or increases the risk of cancer. It is what is called BPH, enlarged prostate or Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia.
BPH enlarged prostate 01
BPH enlarged prostate 02
However, the prostate can also increase in size due to a tumour or cancer, giving the same result or the same problems in practice.
General anatomy of the prostate 01
Since the prostate is so close to the rectum and urethra, an increase in its volume for any of the reasons described above, leads to problems associated with everyday functions such as excretion or erection, as they end up oppressing, obstructing or irritating contiguous areas.
Statistically, the size of the prostate with age tends to increase in up to eight out of ten men. It begins in middle age (around 45 years) and peaks in old age (over 80 years). There are many clinical studies that attempt to respond to this event, although the scientific community is still not very clear. Aspects still to be studied, such as cellular aging or the changes produced in the testicles due to a decrease in testosterone, seem to be directly related to the appearance of an increase in size.
Some indications that you may have hyperplasia:
- The "order" that you mentally send to start urinating, becomes more expensive and uncontrollable, it costs more to do it in an orderly manner.
- During urination itself, the leakage of fluid is weak or it is cut off, escaping the patient's control.
- When you finish urinating, the flow does not stop like years ago, but some droplets keep coming out intermittently.
- When you have finished urinating, you may feel that you are still not satisfied and that there is more urine to excrete.
- Frequently feeling like going to the bathroom but then not expelling the expected amount, which can be aggravated at night.
- Pain, discomfort or frequent infections to which there is no apparent explanation, even the appearance of blood in the urine.
The prostatectomy or intervention by which partial or total tissues are removed from the prostate is indicated as a preventive measure against an even greater proliferation of the size of the prostate that can trigger serious consequences, important infections or even death.
Among the different types of prostatectomy, we can define two based on the degree of resection (extirpation, removal) of tissue: simple and radical. When the degree of affectation is mild or moderate, a simple one can be indicated, but when we talk about a degree of affection, or cancer, the prostatectomy is total or radical, removing all the tissue to ensure that the patient can have a longer life expectancy (and quality).
Looking for prices and information?
Use our virtual assistant and receive in your email everything related to the treatments that interest you. Budgets, recovery times, hospitalization, financing possibilities month by month, etc.
In just a few minutes and without any commitment.
En cumplimiento del Reglamento General de Protección de Datos le informamos que los datos por Vd. proporcionados serán objeto de tratamiento por parte de Andromedi con la finalidad de prestarle el servicio solicitado y/o contratado. Los datos no se cederán a terceros salvo en los casos en que exista una obligación legal. Para más información puede consultarla pinchando aquí.
Prostatectomy sequels
During the intervention, in which invasive surgical instruments are used, the deterioration or rupture of the capillaries and nervous tissues adjacent to the prostate cause a series of dysfunctions (partial or total) in the patient’s body:
- Problems getting and keeping a firm and prolonged erection.
- Problems with urine leakage, such as those described above.
- Anal or fecal incontinence and leakage of flatulence.
- Retrograde ejaculation, which occurs when semen that under normal conditions comes out through the urethra, is redirected to the bladder.
- Partial or total loss of fertility.
- Urethral stenosis (abnormal narrowing of the urethra).
Knowing these risks beforehand can help the patient make a meditated decision with his urologist about what type of treatment to adopt, also taking into account his clinical history, age or the severity of the symptoms, and how to prepare beforehand for that treatment and for the consequences it is most likely to bring.
Although the survival rate after prostate cancer surgery is very high, very close to 100%, and the majority of men suffering from this pathology will not die from this disease, there are studies showing that the rates of anxiety and depression in these patients are significantly higher than in other types of cancer.
High levels of anxiety often lead to low sexual satisfaction and multiple symptoms of depression.
What tools do we use to combat urinary incontinence?
- VIDEO: Urine incontinence in men has a solution
Kegel exercises, erroneously reserved only for women, may be beneficial in increasing pelvic muscle tone to help the bladder retain pee more efficiently. We won’t go into too much detail at this point because you can find many guides on the Internet to support these routines.
For men with urge incontinence, medications can help. Some relax muscles to help prevent unwanted bladder contractions. Others block nerve signals to the bladder that cause it to contract at the wrong time. Prescription medications to reduce an enlarged prostate may help with other urinary problems.
Surgery is undoubtedly the most modern, safe and effective solution: Dr. Madurga, a member of the Andromedi team, is a reference in Spain and Europe in the surgical treatment of incontinence. Depending on the severity of the incontinence, different possible techniques are indicated. If there is a lot of incontinence, we opt for the urinary sphincter, and if it is moderate, we opt for the suburethral compression mesh.
After the intervention, a patient who has been implanted with a sphincter must learn how to use it (urinate on demand by manipulating the mechanism) while with the mesh there is no need for manipulation. The material of the mesh is polypropylene while the sphincter is designed in silicone. There are also differences in price, since the treatment of suburethral mesh is cheaper than the sphincter.
What tools do we use to combat the impotence that is produced?
- VIDEO: Everything about penile prosthesis: types, durability, results, surgery and post-operative.
The primary resource for obtaining results is accurate and personalized diagnosis, based on analysis and experience. There is no point in “poking around in fog” jumping from one type of therapy to another if the particularities and nature of each patient and each process of impotence are not understood. Once each case is reviewed in depth, the usual practice in our Seville office is to choose a combined therapy … or as a last resort the indication of a prosthesis.
- Pharmacological therapy (viagra, cialis, virirec, etc).
- Supportive devices, such as vacuum pumps or shock waves.
- Kegel exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles.
- Sexual psychotherapy, in cases where it is expected to be helpful.
- Penile implant or prosthesis by means of surgical intervention.
At Andromedi we believe that we should spend a good amount of time in consultation to inform the patient in detail about the possible sequelae that the removal of the prostate may cause. From the psychological and emotional point of view, it is the ideal way for the patient to overcome the subsequent process with guarantees.
As we have said previously on our website, the anxiety and concern generated by erectile dysfunction or incontinence may increase if the medical team that has handled the case has not reported in detail before the intervention the possible sequelae of an UPR.
BLOG ANDROMEDI
Other articles that may interest you

Testosterone: Essential hormone for success?
5 April 2024
Could Covid-19 decrease penis size?
5 April 2024
Laparoscopic surgery for prostate
26 September 2023

Cavernous body rotation technique
5 April 2024
Laser prostate surgery
22 November 2021
Priapism: definition, causes and treatment
5 April 2024

To whom, how and where can i buy caverject? All about injectable aprostadil work. A solution to erectile dysfunction.
5 April 2024

What is it and how does penile prosthesis or implant work. A solution to erectile dysfunction.
5 April 2024

Why are jelquing exercises or penis enlargement massages so dangerous (and why they don’t work)?
5 April 2024
Xiaflex: the first non-surgical treatment for acquired peyronie’s disease or curved penis
5 April 2024

Getting a thicker penis: is thickening surgery safe?
5 April 2024

“Operating for phimosis does not increase the size of the penis” – One of the most repeated myths
5 April 2024

How is the sexual life of a man with a penile prosthesis? – Advantages and disadvantages of prostheses
5 April 2024

Andromedi opens a new Clinic in the Canary Islands
5 April 2024

Why do men wake up with an erection in the morning?
5 April 2024

Andrology Textbook
5 April 2024
Author
El Dr. Juan Manuel Poyato, con más de 15 años de experiencia médica, es especialista en Urología, Medicina Sexual y Andrología, Es Profesor Externo del Departamento de Fisiología Médica y Biofísica de la Universidad de Sevilla y Coordinador de Urología de la Agencia Sanitaria Bajo Guadalquivir de la Consejería de Salud (Junta de Andalucía).