Frequent causes
What causes it?
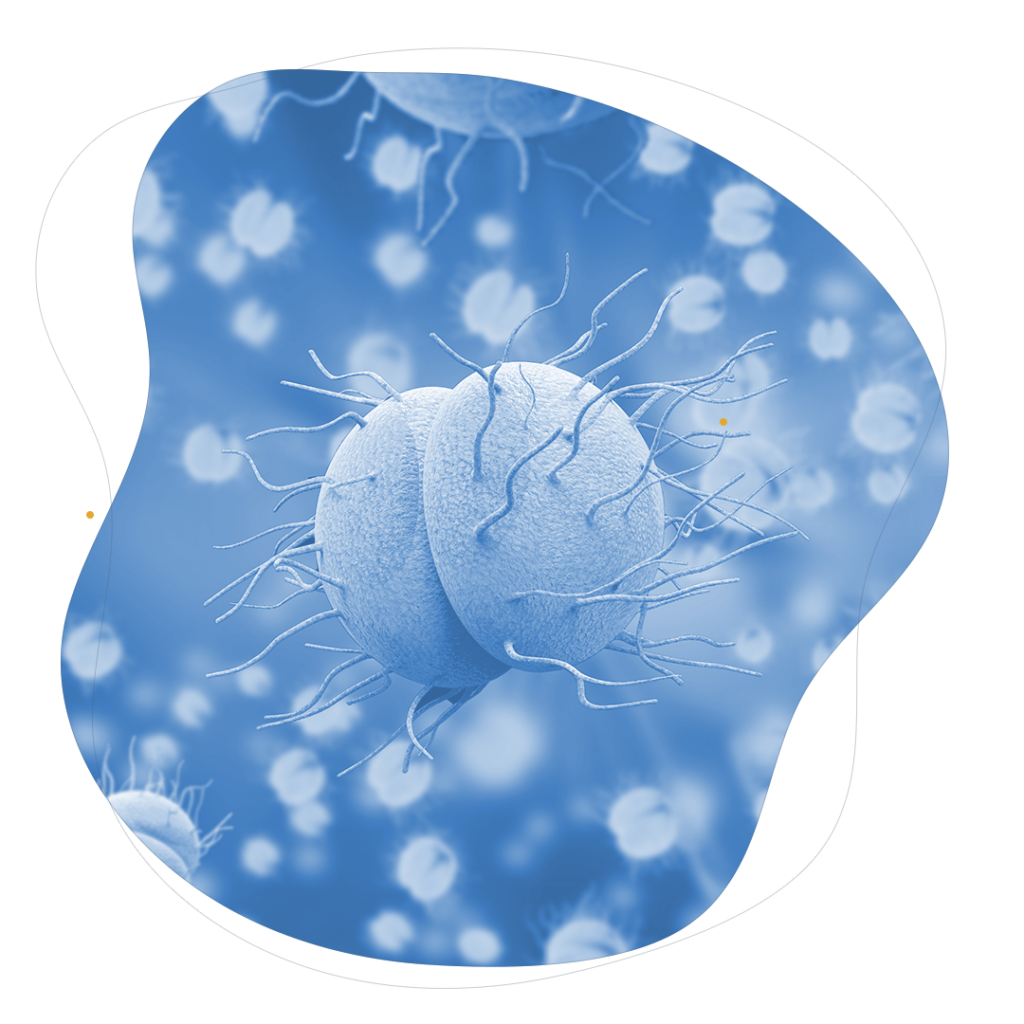
The bacteria neisseria gonorrhoeae is an aerobic microorganism (dependent on oxygen) in the form of small circular dots that form chains, these are diplococci.
This bacteria ferments carbohydrates and gets from them the energy it needs to survive. Laboratory culture is a bit complex because the bacteria can compete for nutrients with other bacteria and die of starvation, so culture media include specific antibiotics for those other bacteria, but not for neisseria gonorrhoeae.
How does the microorganism get sick?
This bacteria invades the epithelial tissues of the urethra (and other mucous membranes of the body) and utilizing thin structures called pili adheres to those epithelials. The immune response is activated and, employing granulocytes, these bacteria are eaten.
However, as it’s an infection little or not at all known to the body, the immune response is insufficient and does not put an end to all these “invaders”, so inflammatory events and secretions are triggered to try to stop them.
How is it transmitted?
It’s transmitted from person to person by direct contact with infected mucous membranes or secretions, especially during unprotected sex.
Transmission can also occur through common sexual practices such as oral or anal sex, in which there are mucous membranes in the same way as in vaginal sex.
The skin itself, has very little susceptibility to bacteria so are rare cases of gonorrhoea on the skin of hands or trunk.

Andromedi pertenece a las organizciones médicas más destacadas en el sector de la Uro-Andrología