Urology TREATMENTS
Artificial Sphincter fo Urinary Incontinence
"Involuntary urine leakage is experienced by millions of people around the world every day. It is a common discomfort that can be solved by artificial bladder sphincter treatment, a novel and effective surgical treatment."
Artificial Sphincter fo Urinary Incontinence
Table of Content
DEFINITION
Introduction to urinary incontinence problems
Urinary incontinence is an embarrassing and annoying condition for many older people. It is translated as the involuntary loss of urine due to anatomical or functional problems of the bladder and urinary tract in men or women. This brings with it an embarrassing decline in the quality of life for hundreds of thousands of people around the world.
Losing urine without voluntary control is a common symptom of many chronic diseases, and therefore each case should be carefully reviewed thoroughly. However, most cases of urinary incontinence do not have a definite cause other than the decrease in muscle tone of the bladder sphincter due to the natural aging process. Research shows that older age does increase the risk of urinary incontinence.
Urine incontinence can affect both men and women in all age groups, especially in older ages. In countries like Spain, this disease has an estimated prevalence of 24% in women and 7% in young men.
In elderly women and men, urinary incontinence can be found in 50% and 29% of all individuals, respectively.
It is important to understand that, although urinary incontinence is very common and that many people decide to shut it up and not seek professional help, this condition can be treated.
For a long time, treatment options for urinary incontinence consisted solely of drug therapy (quite risky in many cases) and pelvic floor exercises (better known as Kegel exercises) but today, scientific advances have found faster and easier ways. effective ways to treat urinary incontinence through other procedures and one of them is the artificial sphincter of the bladder, a novel and effective surgical treatment.
Looking for prices and information?
Use our virtual assistant and receive in your email everything related to the treatments that interest you. Budgets, recovery times, hospitalization, financing possibilities month by month, etc.
In just a few minutes and without any commitment.
En cumplimiento del Reglamento General de Protección de Datos le informamos que los datos por Vd. proporcionados serán objeto de tratamiento por parte de Andromedi con la finalidad de prestarle el servicio solicitado y/o contratado. Los datos no se cederán a terceros salvo en los casos en que exista una obligación legal. Para más información puede consultarla pinchando aquí.
What does the artificial sphincter do?
Treatment Summary
The artificial sphincter prevents involuntary loss of urine in patients with urinary incontinence. It is a highly effective and reliable method to treat this condition. You can receive treatment at any of our centres in Madrid, Seville or Tenerife.
What does the artificial sphincter consist of?
It is a high-tech medical device that consists of a silicone sleeve that surrounds the urinary urethra to prevent leaks or leaks. It consists of a mechanism that allows you to compress or relax the urethra to allow flow during urination.
What is implatation surgery like?
The surgeon makes only two incisions, one at the base of the scrotum and one in the skin of the belly (lower abdomen) to insert not only the urethral cuff but a reservoir of fluid and a small pump. In the end, the surgeon closes the incisions and the procedure is finished.
Results
Evidence shows that more than 90% of all patients who received this treatment were able to eliminate urinary incontinence problems. Very low complication rate.
How is the sphincter used?
To urinate, the patient only has to press a small pump located under the skin of the scrotum to relax the artificial sphincter and allow the bladder to empty. In less than two minutes, the sphincter closes on its own.
Type of anesthesia
The anesthesia used is of a general type. The surgery lasts less than two hours and the patient must remain hospitalized for one day. Then you must rest for a few days.
Frequent Causes
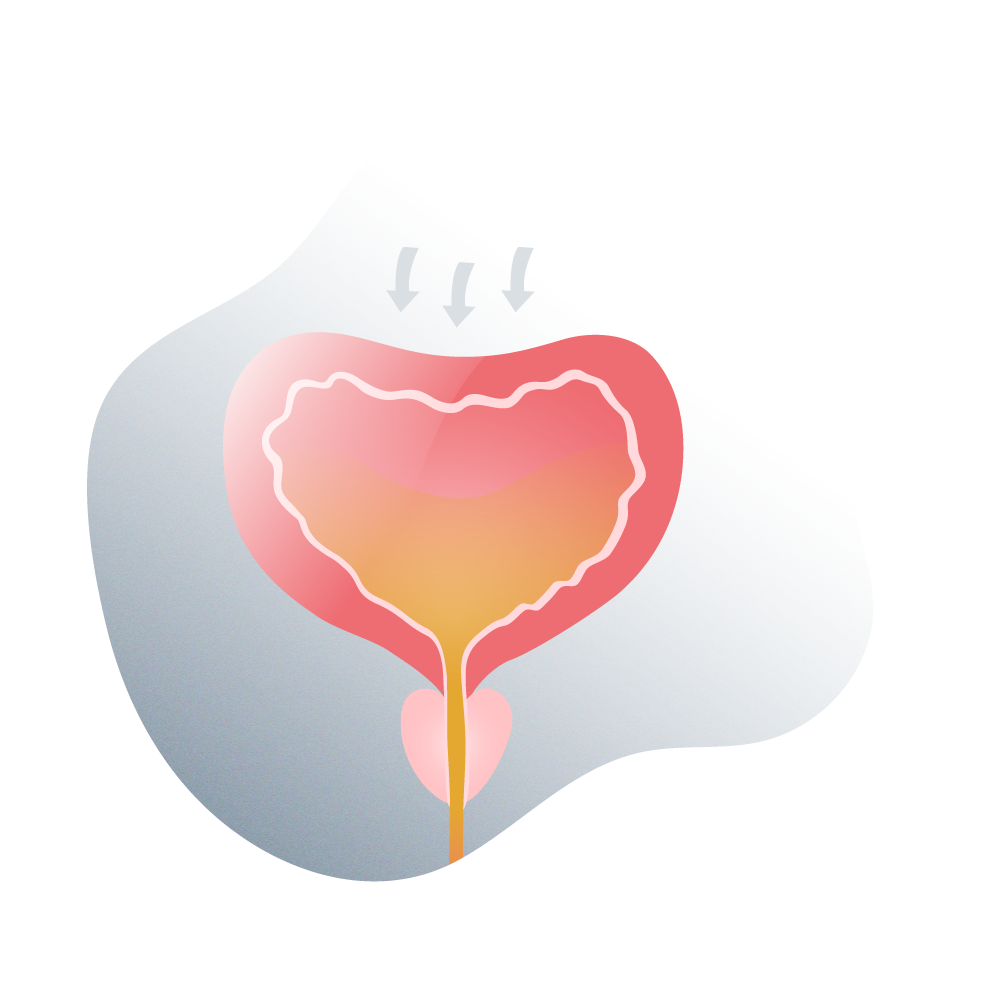
What is an artificial sphincter for urinary incontinence?
The artificial sphincter for the bladder is a medical device made with special rubber that is placed at the base of this organ and in this way treats urinary incontinence problems caused by different causes.
This device (the artificial sphincter) is shaped like a ring and is placed around the urethra, just below the urinary bladder. This ring has the ability to inflate voluntarily with the help of a small insufflation handle and in this way, produce urethral pressure and prevent urine from escaping from the bladder.
The insufflation handle controls the urethral ring and allows it to constrict or relax at will depending on whether the patient wants to urinate (relaxes the ring) or wants to prevent urine from escaping and soaking the underwear (something quite annoying) for which the ring tightens.
The artificial sphincter is inserted into the body of the patient and for this reason requires a surgical intervention of medium to low complexity, with few associated risks and with an improvement rate close to 100%.
In our Andromedi Clinics in Madrid, Seville and the Canary Islands, we always study the specific causes of each patient in order to offer the most appropriate treatment.
How composed is the artificial sphincter?
This high-tech medical device consists of three essential parts:
1 Urethral occlusive cuff: A small, hollow, circular, silicone ring that is located through the urinary urethra. This is the component in charge of preventing urine leakage.
2 A reservoir balloon, also made of tissue-friendly material, that contains a small amount of saline solution. This balloon is surgically located within the pelvic area of the patient and is completely imperceptible.
3 Control pump: A cuff that inflates saline solution from the balloon into the ring or regulates the exit of this fluid from the ring to relax the urethra and make urination possible.
These three components are joined together by means of a short and thin plastic tubes that are hypoallergenic and safe.
What must the patient do to urinate?
To urinate, the patient only has to press the tiny artificial sphincter control pump hidden in his scrotum to move the fluid from the urethral cuff to the balloon (located in the abdominal part). This will relax the cuff and the urine will flow freely to the penis (or vagina).
The cuff remains open for about three minutes, long enough to completely empty the bladder, and then the cuff automatically refills with fluid and the urethra is occluded.
Patients
Who are candidates for this treatment?
This medical device is implanted in patients with a history of severe urinary incontinence, resistant to drug treatment (there are medications for this condition but they have too many side effects) and with associated pathologies that aggravate the condition, such as in patients undergoing extprostate irpation due to cancer or benign hyperplasia.
The implantation of the artificial sphincter is carried out in cases such as:
Stress incontinence originating
Stress incontinence originating after prostate surgery in which the bladder sphincter may have been injured or some nerves responsible for regulating the flow of urine have been accidentally cut.

Stress incontinence originating
Severe urinary incontinence in which conservative treatments failed or were insufficient. The quality of life of the patient is limited.

Severe urinary incontinence

Leakage of urine from the bladder
Leakage of urine from the bladder due to loss of sphincter muscle tone: this occurs in elderly patients and is usually quite common.

Leakage of urine from the bladder

Benefits and advantages
Benefits and advantages of the artificial sphincter

Quick recovery
The placement of the artificial sphincter for urinary incontinence is a relatively simple procedure with which the patient can return to their daily activities in a few days. Most of the time, the recovery lasts a week but after this time, the patient needs to continue avoiding great efforts.
However, it is not necessary to take a long time off from work as with other surgeries.
• Immediate improvement
The patient can experience the definitive improvement of incontinence problems as soon as the doctor indicates it. Generally about six weeks after surgery because the healing process needs to be completed correctly before activating the device for the first time.
No more drugs
The medications indicated for urinary incontinence are not only ineffective but also bring with them countless and potentially dangerous side effects such as tachycardia, nervousness, insomnia and dizziness due to hypotension (depending on the drug). The improvement of urinary incontinence with the artificial sphincter is achieved completely and the patient can do without using this type of medication.
No more adult diapers
One of the reasons that urinary incontinence is so bothersome, and in some cases a cause of depression or social embarrassment, is the need to wear adult diapers.
These diapers are often effective at containing unintentionally leaking urine but must be changed constantly, are expensive, and most are noticeable under clothing. Many adults with urinary incontinence who wear diapers may even experience a rash and skin irritation in the genital area.
The artificial sphincter avoids this completely as there is no more leakage of urine and therefore the patient can return to wearing normal underwear with the confidence that unwanted accidents will not occur.
Definitive treatment for urinary incontinence
Neither medications, nor pelvic floor exercises, much less adult diapers offer a definitive solution for urinary incontinence in adults.
Surgical treatment with implantation of an artificial sphincter for the bladder or bladder mesh are the only truly effective options, referring to the ability to contain and prevent any urine leakage (however minimal) as long as the patient is not voluntarily urinating.
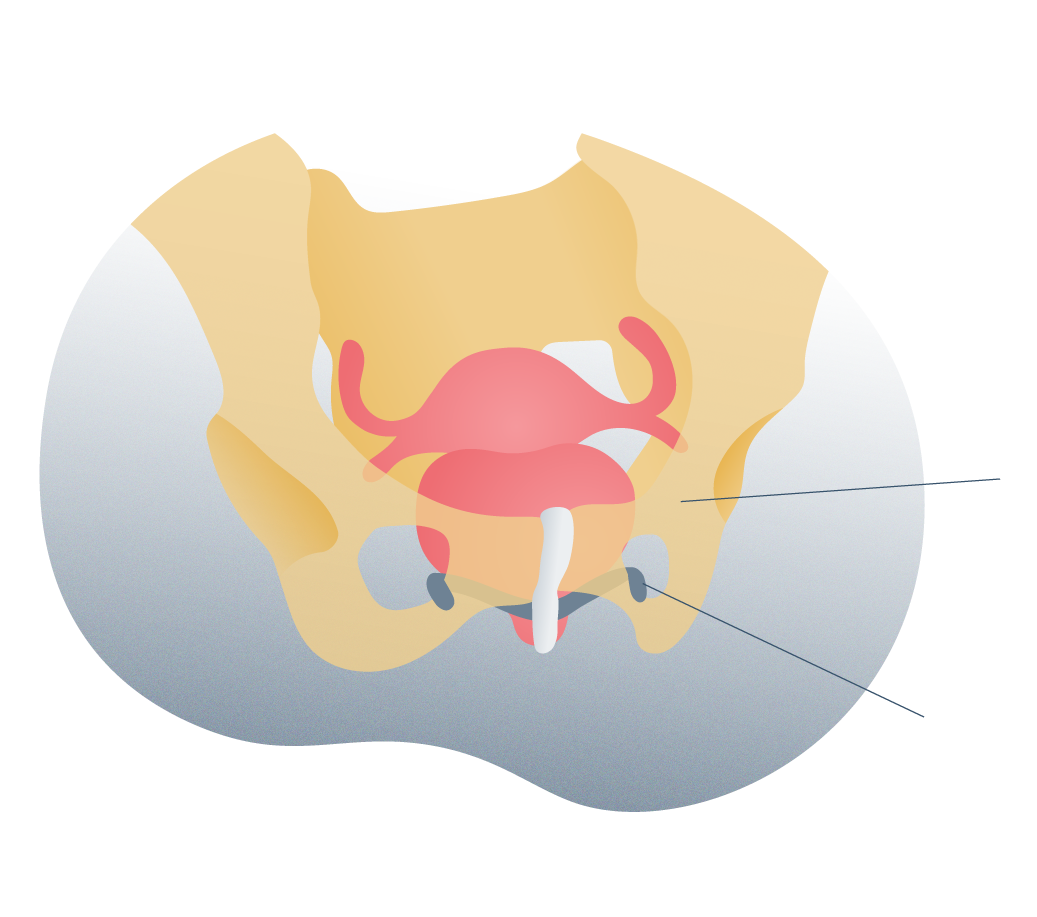
Male suburethral mesh surgery
Surgery
What does the surgery consist of?
The surgery to place an artificial sphincter for urinary incontinence is a relatively short procedure, in less than an hour it is possible to surgically insert the device into the patient’s body.
Preparation for surgery
Before surgery, the patient must undergo a preoperative evaluation so that the treating physician examines his general state of health, the rate of urinary continence (how much urine he is able to withstand before there are urine leaks) and determine if the patient can receive the intervention.
Preoperative evaluations often include:
- Medical interview.
- Physical examination and urinary function.
- Blood tests.
- Anesthesia sensitivity tests.
The step by step of the intervention
During the surgery and after placing anesthesia, the surgeon in charge of the operation (and trained to implant the device inside the body) makes two short and straight incisions:
One of them in the space between the anus and the scrotum (or perineal raphe).
The other incision is made in the lower abdomen, at the level of the belly.
Through the first opening at the base of the scrotum or the bag that supports the testicles, the surgeon places the control pump that will then serve to relax the artificial sphincter and, through the second incision (slightly larger than the anterior) on the lower abdominal wall, the urethral cuff and the balloon that stores the fluid is placed. The urethral cuff is placed close to the bladder neck.
At the end of this process, the parts are connected to each other and the surgeon checks that everything is fine before moving on to the last part of the surgery: the suture of the skin that has been cut.
Each surgeon has different techniques surgical procedures to perform this procedure and he can decide which one is ideal.
This suture thread has the peculiarity that it dissolves on its own after a while and the body absorbs it without any problem.
A Foley FEB-type urinary catheter may be inserted after artificial sphincter surgery to drain urine from the bladder and prevent compression of the urethra and abdominal muscles. Bladder catheter placement helps tissues heal more easily.
Postoperative care
The patient can return home about 24 hours after surgery (the hospital stay is short) and must take special care of certain aspects such as:
- Hygiene of surgical wounds, which includes washing them with mild soap and water, of neutral pH.
- It is necessary to replace the bandages that cover the operative wounds with new ones from time to time, at least after the first 48 hours.
- For a week the patient must use scrotal support (or scrotal bag support) to prevent the scrotum from hanging too freely and can be injured.
- It is recommended to avoid strenuous activities for at least 6 weeks after surgery. These activities include running, jumping, biking, playing sports like soccer, lifting heavy weights from the ground, or going to the gym.
- It is recommended that the patient abstain from sexual intercourse for a reasonable period of time, which may vary. The urological surgeon will be the one to decide how long is appropriate without sexual intercourse, including masturbation.
- After surgery, some medications such as pain relievers, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and antibiotics are indicated to prevent infections, especially since it is a region exposed to urinary tract pathogens.
- In patients with constipation problems (constipation), laxatives are recommended to soften the stool and prevent stress overload on the abdominal wall.
When should I go to the doctor?
Generally, the first postoperative evaluation visit (if no warning signs develop) is during days 7 and 14 after surgery.
However, if the patient notices abnormal changes or symptoms of infection or bleeding, they should receive immediate medical attention from the urologist.
Among the main warning signs are:
- Fever equal to or greater than 38 ° C.
- Bleeding through urine or incisions.
- Persistent pain (not relieved by pain relievers or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
- Feeling of difficulty urinating (when the patient must make a great effort to urinate).
- Feeling of pain in the bladder, as if it were very full.
What kind of anesthesia is used?
During this surgery the patient receives general anesthesia. This explains why this procedure is completely safe and painless.
If a patient is allergic to anesthesia before surgery, it can be determined through sensitivity and hypersensitivity tests to different ones.

Immediate improvement
Results

After surgery to implant the artificial bladder sphincter to treat urinary incontinence, the patient must stay at least one day in the hospital so that the effect of the anesthesia passes and the doctor can assess the state of health and allow discharge.
Most patients leave the hospital during the first 24 hours after the intervention.
Regarding the concrete results of this treatment and the real efficacy of the artificial sphincter, a study conducted in 2012 in the United States of America showed that this procedure has astonishing levels of success in cases of moderate and severe urinary incontinence.
Between 90 and 100 % of all patients with incontinence achieve immediate improvement after implantation of the artificial sphincter.
Risks
The risk of complications associated with the artificial sphincter to treat urinary incontinence is mostly related more to the implantation surgery itself than to the device itself.
All surgeries carry a certain rate of complications, especially in patients with poorly treated chronic diseases (diabetes, for example). Some of them are more complex than others and therefore complications can be more frequent and severe.
Fortunately, in this surgery, the degree of complexity is not so high and the risks are very low. Few patients develop severe complications and it is easy to compare with the incredible positive results that the artificial sphincter achieves.
Among the possible complications that can be found after a surgery of this type are:
These infections usually resolve within a couple of weeks with antibiotics. They are infrequent but can occur, especially in pacieThe very old or those with immune problems, such as those who take steroids (medicines that decrease the body's immune response).
(which are usually very small), mainly in patients taking anticoagulant medications such as aspirin or warfarin. It is important to talk to your doctor before surgery about all medications you take and any previous illnesses, even those that don't seem to matter.
Of all the complications, this is one of the most frequent and occurs because the placement of the artificial sphincter irritates the urethra. This usually resolves on its own within a few days and is not a sign of anything serious (unless bleeding occurs).
Which is usually mild and goes away in a few days. It happens because the artificial sphincter pump is a "foreign body" and can rub on some nearby organs or the abdominal wall itself.
And finally, a complication much less frequent than the others:
- Urinary device failure (rare complication)
In some cases (very few), the urinary sphincter may fail for mechanical reasons such as compression of the tubes that inflate the urethral ring or a defect in the pumping device inside the scrotum. If this happens, the patient should go to the doctor to evaluate the condition of the artificial sphincter and if it is necessary to replace it with a new one. A fully functional device does not even allow urine dripping.
Diagnosis
Urinary incontinence: causes and diagnosis
Before we stop to define the causes and how urinary incontinence is diagnosed, it is essential to understand normal urinary anatomy and how an artificial sphincter can solve any problem of inadvertent urine leakage.
The urinary sphincter
The urinary sphincter is a circular, ring-like muscle that surrounds the urethra below its junction with the bladder (the place where urine produced by the kidneys is stored) in women or below the prostate in men. . The urinary sphincter is in an area known as the bladder neck.
If the urinary sphincter is contracted, the caliber of the urethra is also compressed and urine does not flow. This occurs most of the day while the person is sleeping or awake. However, urine accumulates in the bladder until it warns the autonomic and central nervous system about the need to eliminate that urine through urination.
When this happens, the nervous system produces two opposite effects: the relaxation of the urinary sphincter and the contraction of the detrusor muscle of the bladder. Only if both occur at the same time in a coordinated manner (especially sphincter relaxation), can urine flow voluntarily and the individual feels calm from having gone to the bathroom and can continue with their daily tasks.
Yes, and the reasons can be several. From psychological disorders such as nervousness to pathological problems such as degeneration of the nerves that control the muscles responsible for urination due to diabetes (diabetic neuropathy), radiation therapy for prostate cancer or surgery to remove this gland.
Causes and diagnosis of urinary incontinence
Given the large number of physiological mechanisms that are responsible for making urination possible, the causes of urinary incontinence can be multiple and the degrees of affection on the patient’s quality of life can vary.
The most common cause of urinary incontinence is aging, in which some urethral erosion and in some cases, urethral atrophy may develop. Both abnormal processes decrease the ability of the bladder and urethra to hold urine at times when the patient is urinating, thus urinary leakage ensues. Over the years, the risk of incontinence increases progressively.
In men, an enlarged prostate produces a type of incontinence known as overflow incontinence.
What is stress incontinence?
It is one of the most common types of urinary incontinence and occurs when pressure inside the abdominal cavity suddenly increases and the bladder sphincter is insufficient to hold urine. Sometimes this type of urinary incontinence can be associated with overflow incontinence (mixed incontinence).
Questions and Answers
Frequently asked questions at the Andromedi centers in Madrid, Seville and Tenerife
Yes, but this may only be possible after the patient has duly completed the recovery process indicated by the treating physician. Before this, having sexual intercourse could be a dangerous practice as the patient could injure or reopen the operative wounds.
Some patients feel a valid concern about the aesthetic appearance of the genitalia after the implantation of the artificial sphincter, however, it is practically impossible to distinguish with the naked eye if someone is wearing it or not. The implanted device is located under the skin and is not marked or obvious.
Except for the day that the patient must remain in hospital for medical observation, absolute rest is necessary for a few days (less than a week). After that time, the patient can gradually return to their daily activities, avoiding as much as possible heavy tasks or those that could damage operative wounds.
Yes, it needs to be replaced after a while. Generally, the useful life of the device is 8 to 10 years and after that time, the patient must attend a consultation to evaluate the quality of the sphincter and if he is still competent.
Obviously, if before this time the patient experiences artificial sphincter failures such as urine leakage or difficulty urinating, she should go for a urological evaluation immediately.
Yes, and it is recommended that the patient remain with the probe for a reasonable time, usually a week or perhaps earlier to allow the tissues to heal.
This time can vary but it is almost always possible to start using the artificial sphincter 6 to 8 weeks after surgery.
Medical references and bibliofraphy
- Artificial Sphincter for Urinary Incontinence in Men University of Michigan
- Male urinary incontinence: Artificial sphincter Scielo
- Artificial urinary sphincter placement: Innovations and practices Mayo Clinic
- Prostate Surgery Intuitive Inc.
- Artificial Urinary Sphincter for Postradical Prostatectomy Urinary. Incontinence — Is It the Best Option? U.S. National Library of medicine
- Urinary incontinence: What you need to know Medical News Today
Author
Natalio Cruz MD, with 25 years of medical experience, has been until 2016 Head of the Andrology Unit in the Urology Service of the Virgen del Rocío Hospital in Seville, National Coordinator of Andrology in the Spanish Association of Urology (AEU) and General Secretary in the ESSM, positions that he has narrowed to focus squarely on this exciting project of offering a high-level private medical consultation in Marbella, Seville, Madrid and Tenerife.
Andromedi pertenece a las organizciones médicas más destacadas en el sector de la Uro-Andrología