Techniques and treatments
Phimosis treatment and solution
· Surgical treatments: Circumcision is not the only option ·
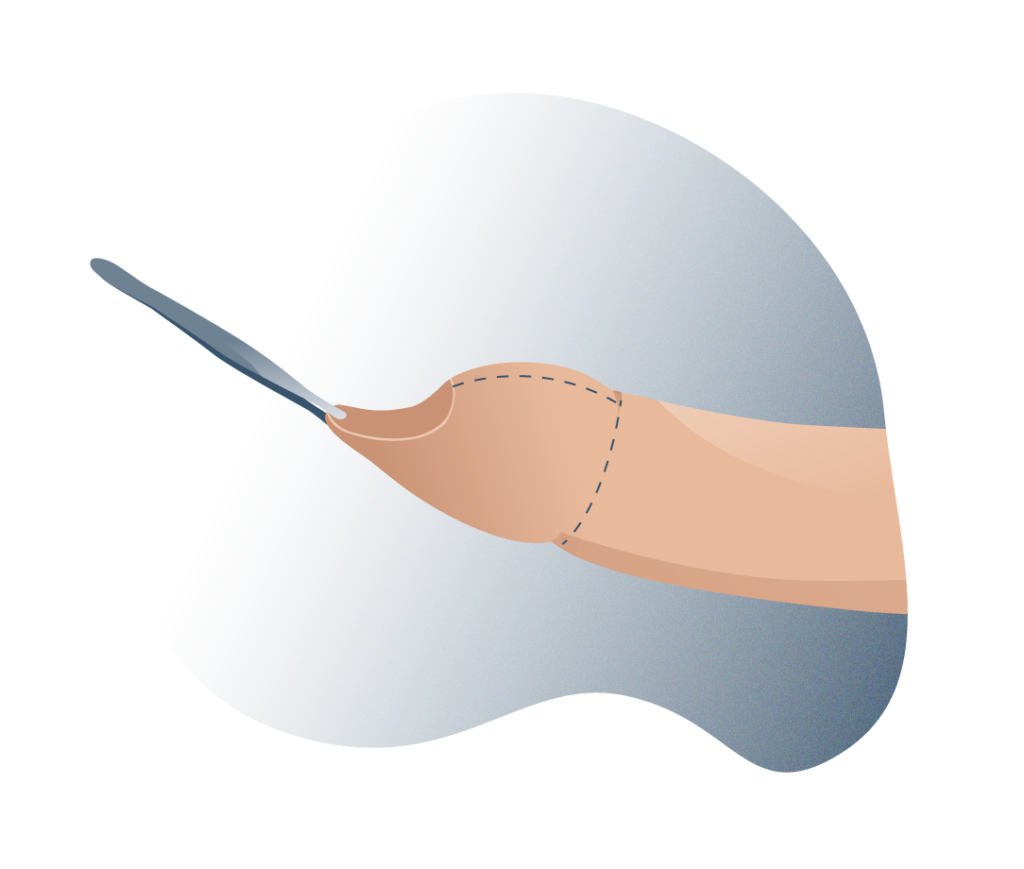
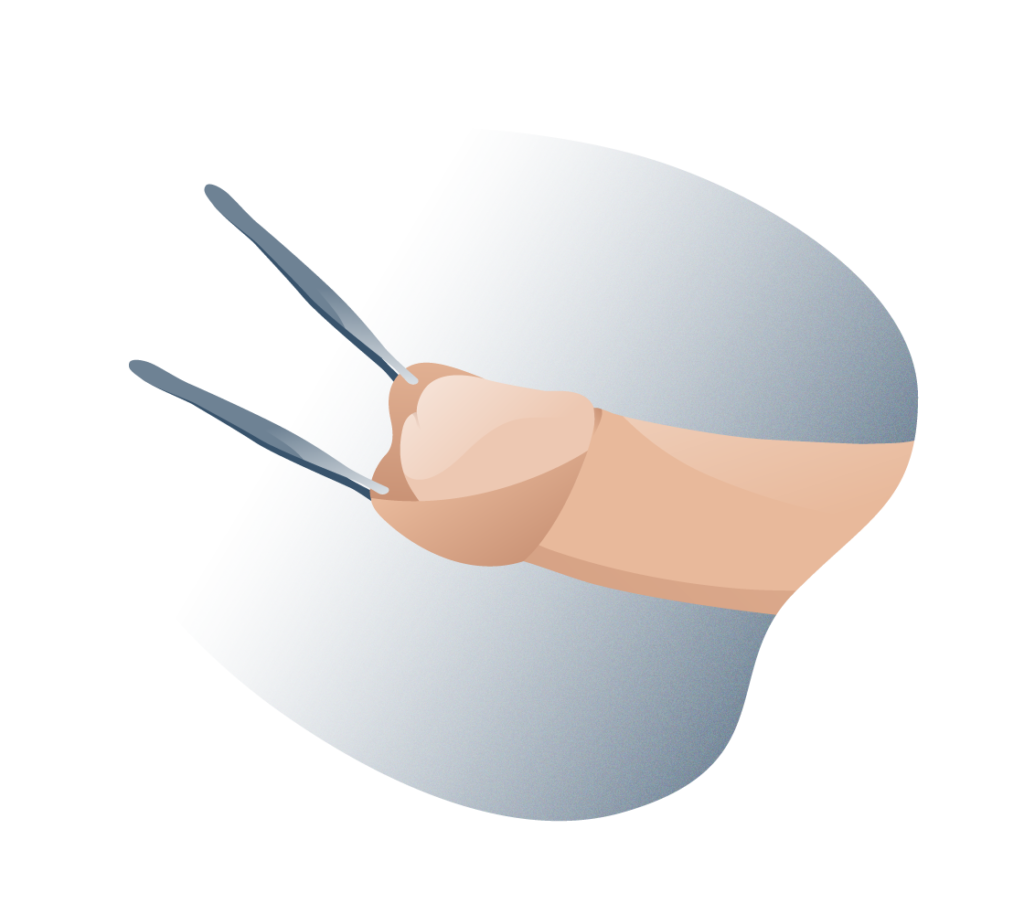
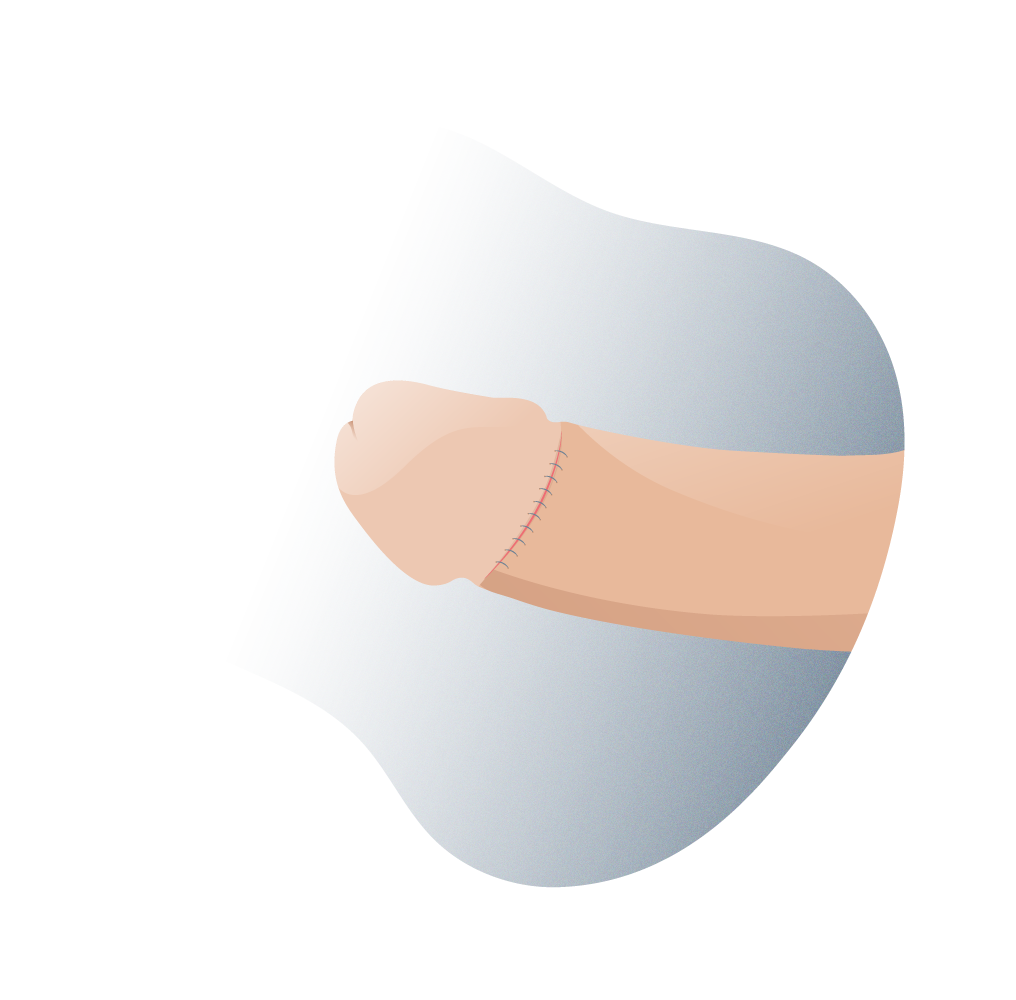
Circumcision is a common surgical practise, much more so among certain cultures and religious communities (such as Jews or Muslims) that consists of the partial or total removal of the foreskin, leaving the glans permanently exposed. It is a relatively simple surgical procedure that can even be performed in the child’s first months of life. Apart from circumcision, there are other surgical options in the treatment of phimosis:
Preputioplasty consists of a longitudinal incision over the constriction band of the foreskin, leaving it practically intact. It is less painful than circumcision and involves less recovery time.
A dorsal slit or superincision consists of a single incision on the upper surface of the foreskin, from the tip to the crown, exposing the glans and reducing unnecessary tissue removal to zero. A ventral slit or sub-incision also exposes the glans but through an incision of the foreskin in its lower portion, which goes from the tip of the frenulum to the base of the glans, this operation is performed when phimosis is accompanied by a short frenulum.
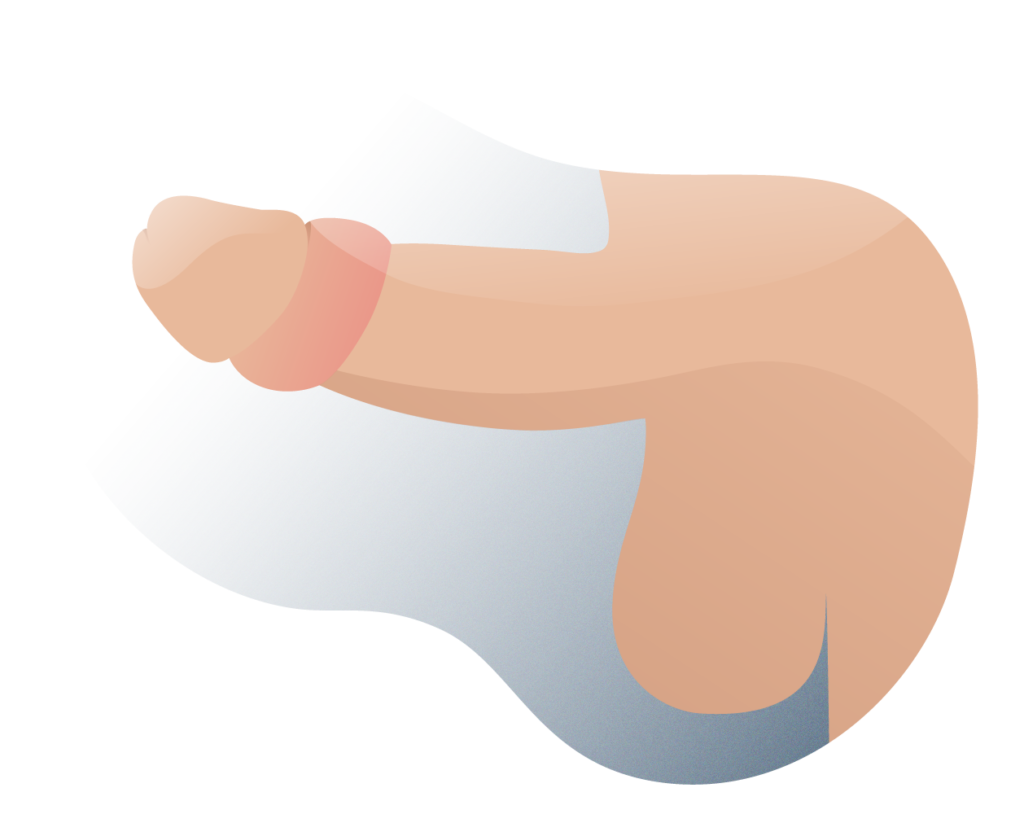
Technical phimosis
Technical phimosis
Technical phimosis
Surgical treatment of phimosis is indicated only after non-surgical methods (which we will see below) failed or were insufficient. Also, in cases where there is imminent danger of tissue loss (by cell necrosis) or total narrowing of the urinary meatus.
Dr Pedro Lopez Pereira, a renowned urologist who has treated hundreds of children at the Hospital de La Paz in the Community of Madrid in his long experience, is the head of our Paediatric Unit and performs all the interventions and monitors the results.
There are non-surgical ways to treat it, and in fact, they should be a priority.
Phimosis can be treated without the need for an operating room; the method of choice is topical application of corticosteroid cream (such as 0.05 per cent betamethasone, twice daily for a period of two to eight weeks).
These drugs work by decreasing the inflammatory immune responses at the site and improving the elasticity of the skin with the synthesis of new elastic and collagen fibres, allowing the progressive reduction of phimosis.



Andromedi pertenece a las organizciones médicas más destacadas en el sector de la Uro-Andrología